1. Searching Database
Searching through MERITS is fairly straightforward. In MERITS, we have provided several search options to facilitate fast data retrieval from MERITS.
(1) Searching with Protein Id and Locus.
The MERITS database includes 22,353 proteins that can be linked to the NCBI database. Specifically, there are two search methods available for ID search: Protein ID and locus search. A Protein ID is a combination of six to fourteen letters and digits, while a locus search consists of eight to twelve letters and digits.

(2) Searching with Keywords.
Furthermore, our platform offers the option to search by organism or definition. To assist users in formulating their search criteria, they can select the "Example" button to retrieve a list of sample keywords.
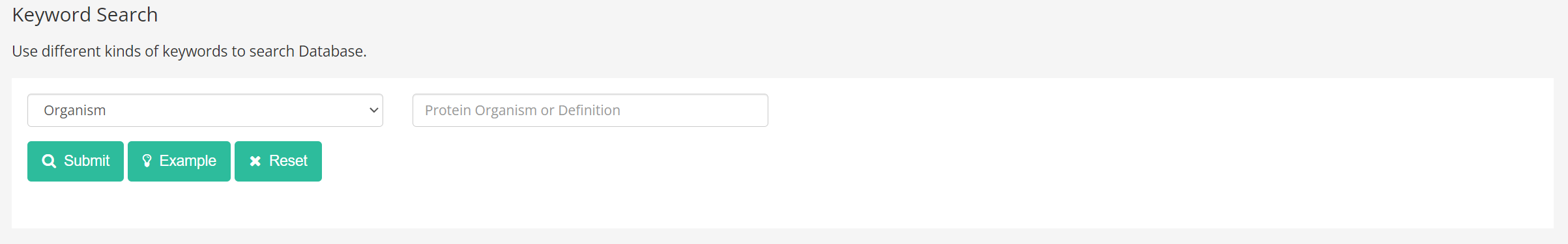
(3) Searching with multiple keywords.
Ultimately, our platform offers a sophisticated search feature that enables users to select from an array of search parameters and retrieve the desired data by clicking the submit button.
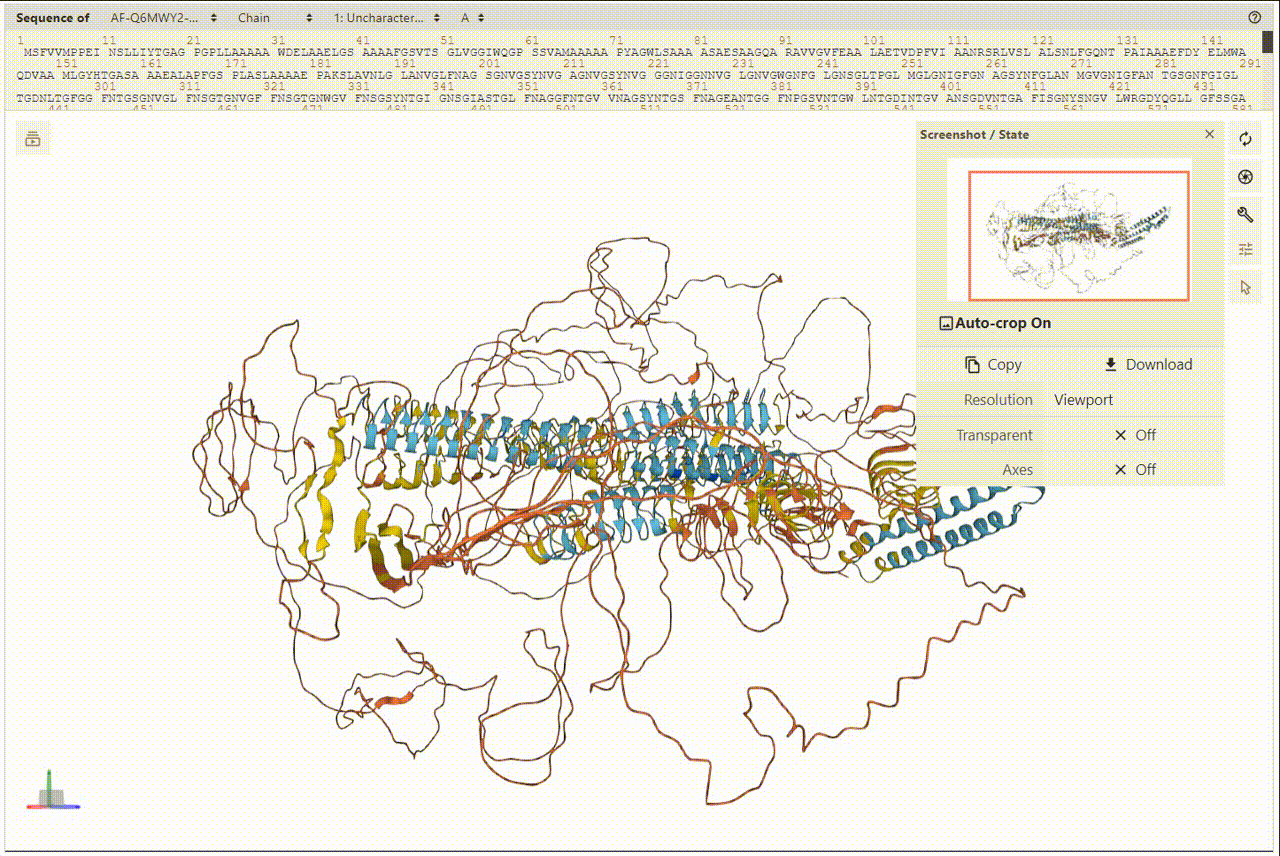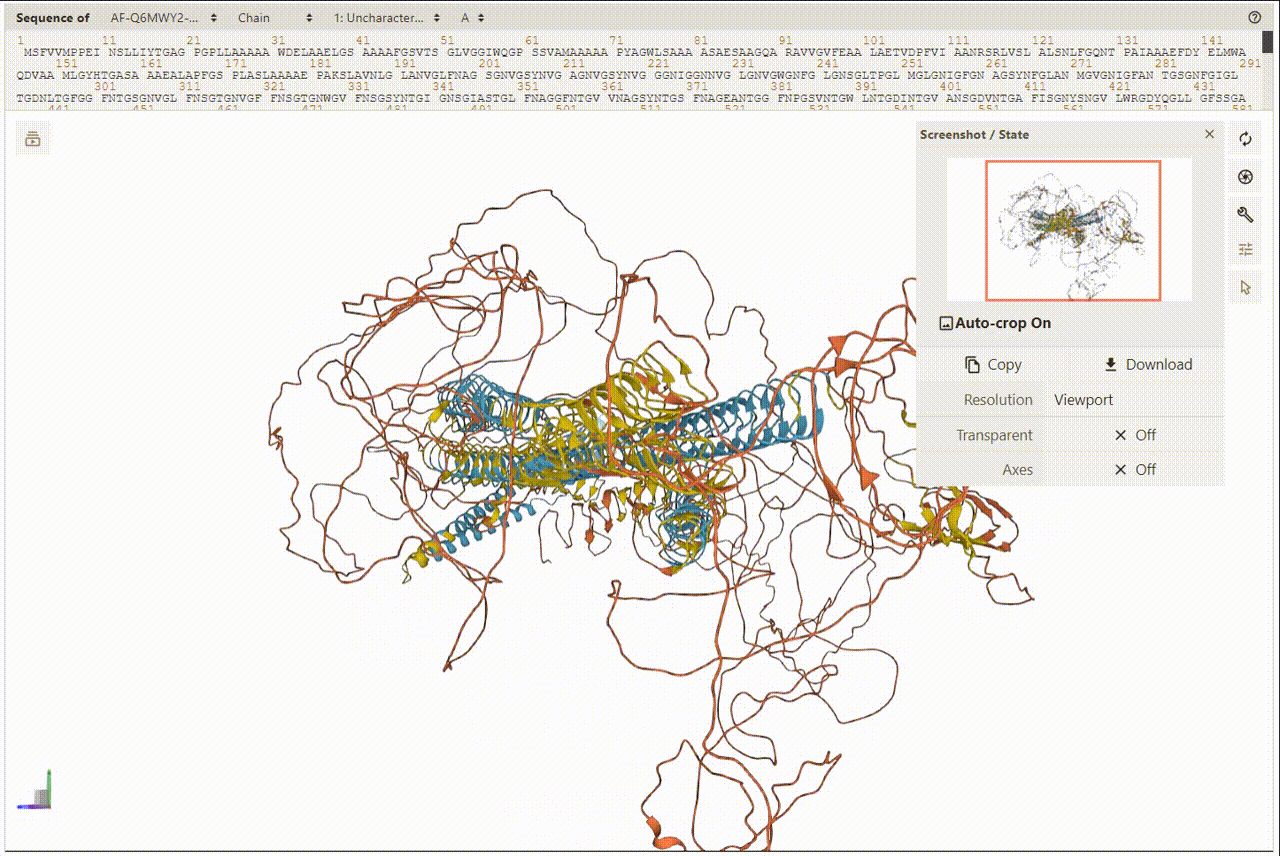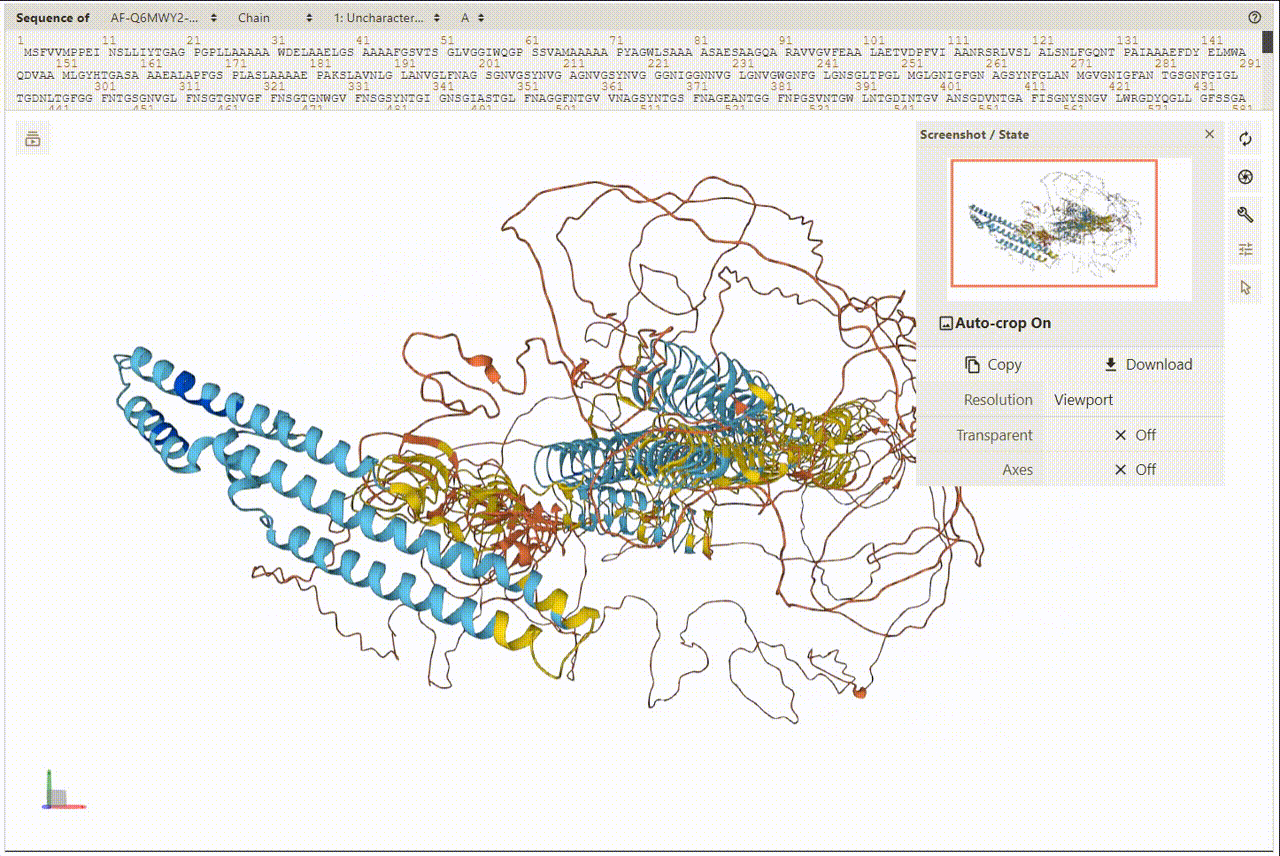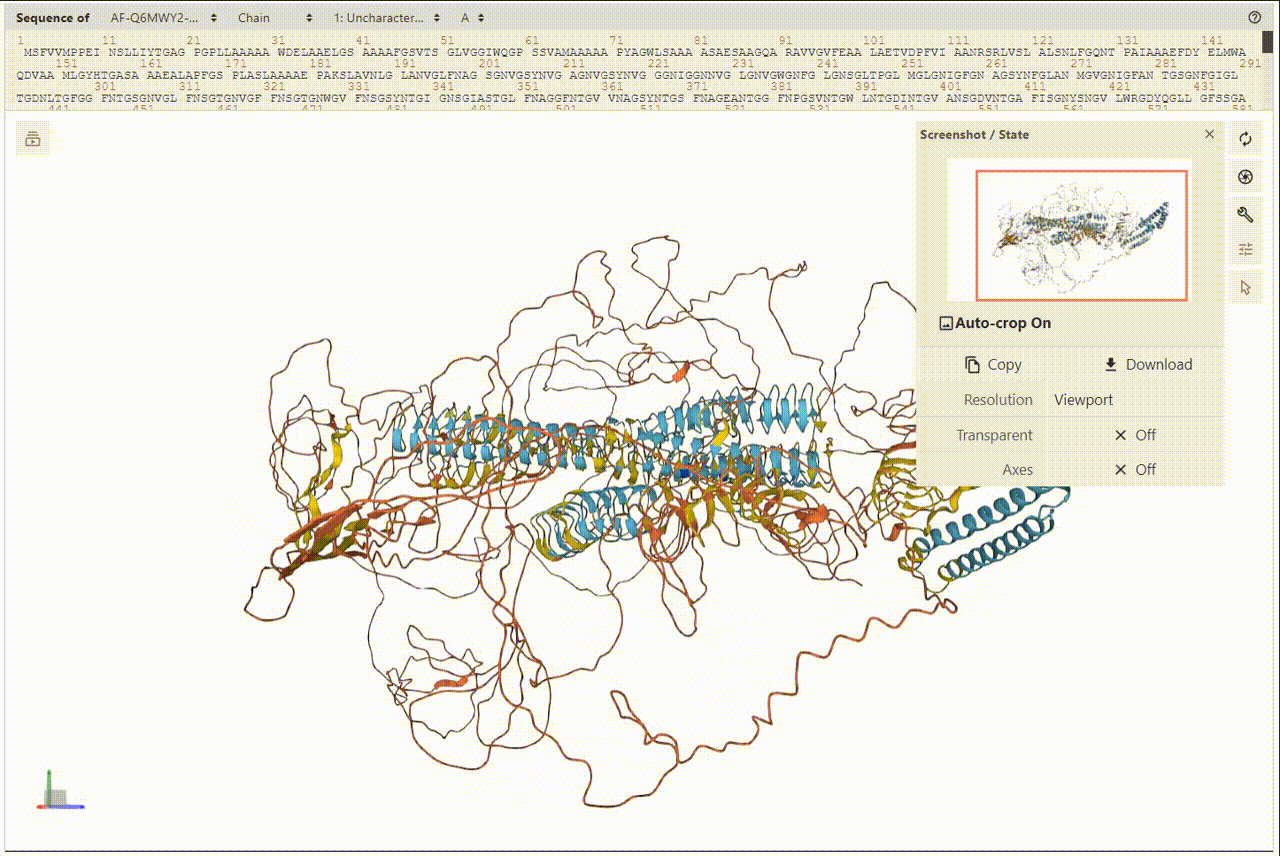
2. Overview of Protein and Structures
PDBe was utilized for presenting and visualizing protein structures. Additionally, PDBe facilitates a superposition view that overlays observed ligand molecules on representative protein conformations. To view the 3D structures, users can access the detailed information page.
3. The basic physicochemical properties
To derive the physical and chemical properties of proteins stored in MERITS, we rely on ProtParam. This tool enables computation of a suite of parameters, including molecular weight, theoretical p value, atomic composition, extinction coefficient, estimated half-life, instability index, aliphatic index, and grand average of hydropathicity. Results of ProtParam analyses can be viewed on the detailed information page.

4. The hydrophobicity information
Additionally, we utilize ProtScale to calculate and depict the amino acid scale profile on a specific protein.

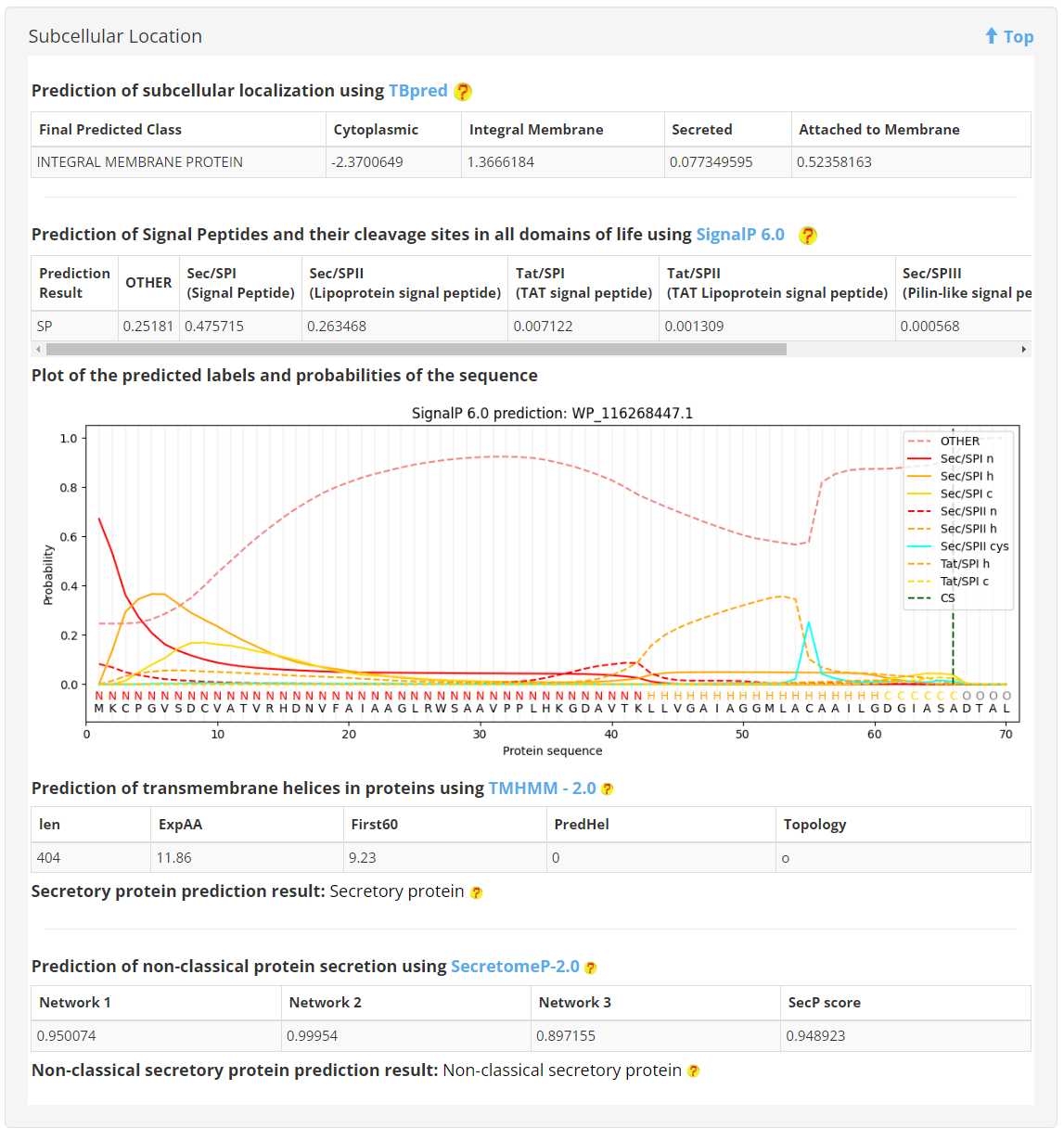
5. Subcellular Location
Initially, subcellular localization was predicted using TBpred. Subsequently, signal peptides and transmembrane helices were identified using SignalP 6.0 and TMHMM 2.0. Finally, SecretomeP 2.0 was utilized to identify whether the protein is classified as non-classical secretory.
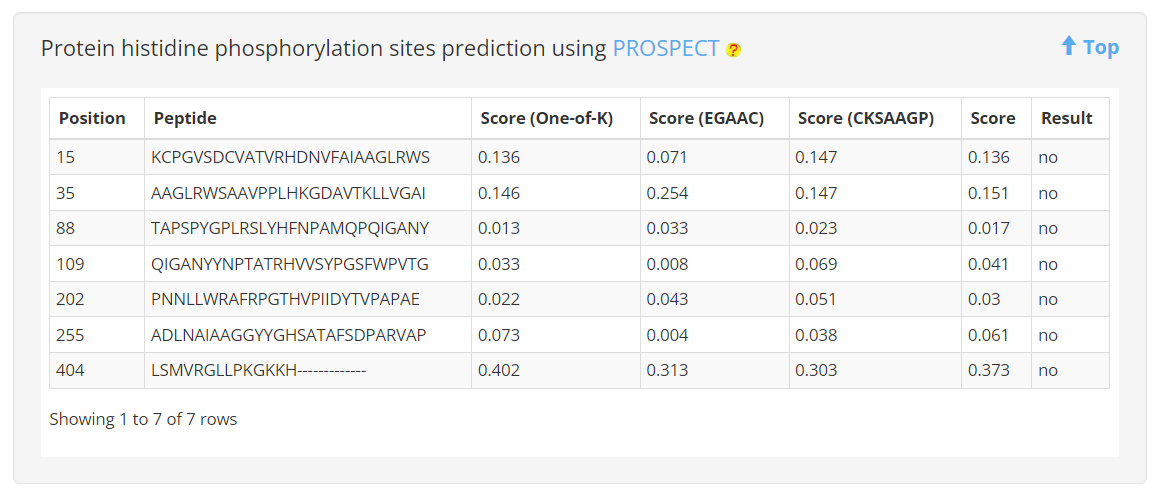
6. Protein histidine phosphorylation sites prediction
The PROSPECT tool was employed to analyze the histidine phosphorylation sites of proteins within MERITS. The predicted results were subsequently obtained and provided to users as a reference.
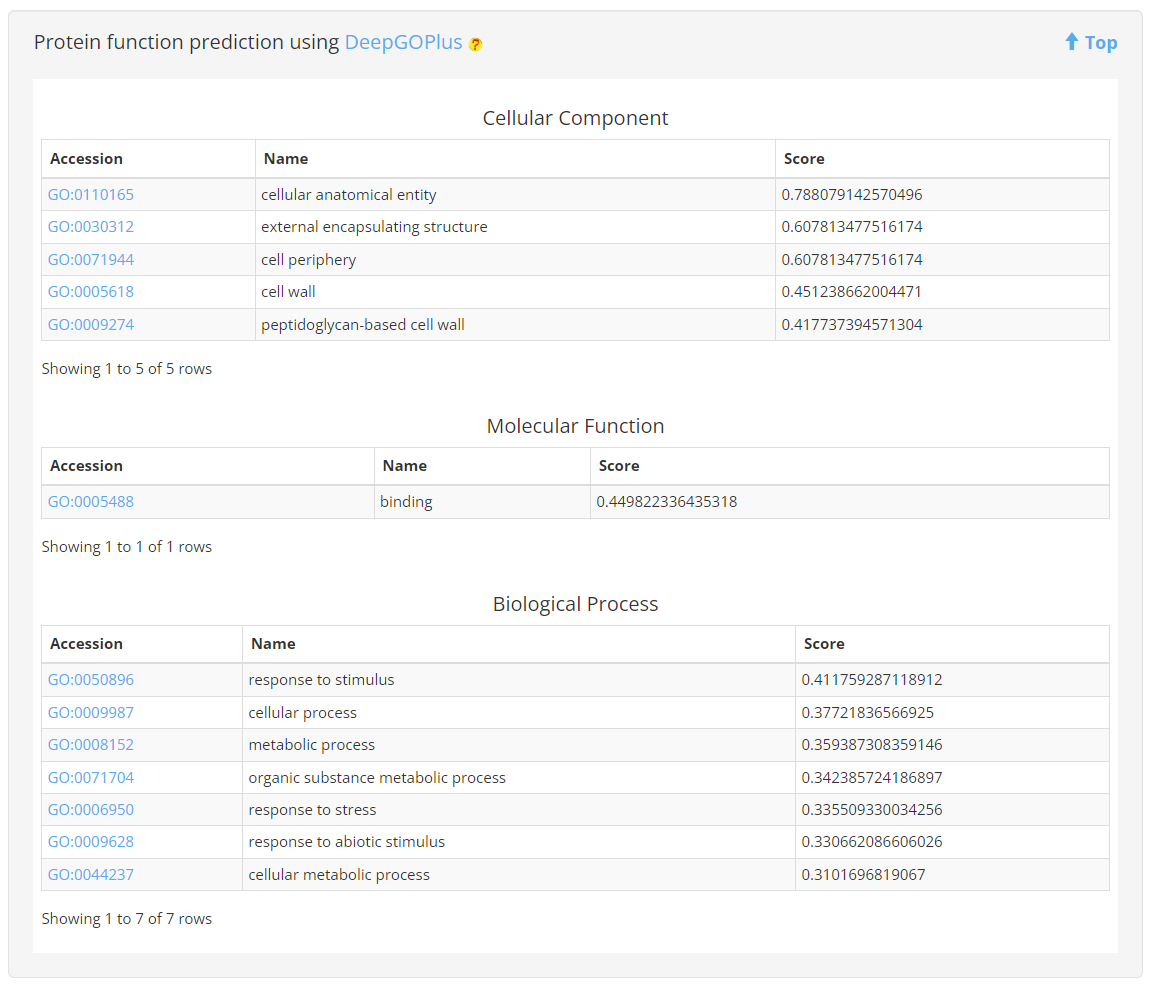
7. Protein function prediction
DeepGOPlus was utilized to predict protein functions, which included GO terms from the Biological Process, Molecular Function, and Cellular Component sub-ontologies, along with their respective confidence scores.
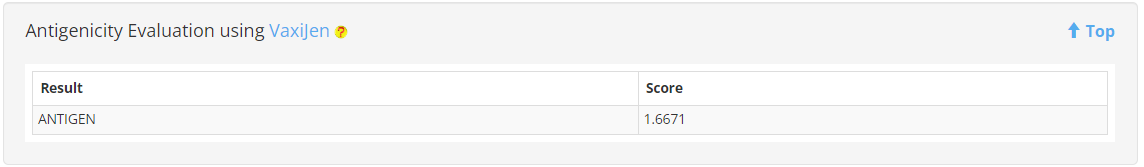
8. Antigenicity, Toxicity and Allergenicity prediction
VaxiJen, Toxinpred2 and AllerTOP were used to determine Antigenicity, Toxicity and Allergenicity of each protein in MERITS.


9. Protein fuction prediction
BLASTp was used to predict homology between PE/PPE proteins and H. sapiens proteins (ref: GRCh38.p14). And blasterJS was used to visualize the results.

10. Linear B-cell epitope prediction
We use ABCpred to predict B cell epitope(s) in PE/PPE proteins' sequence.

11. Secondary Structure of Protein
The NetSurfP - 3.0 Model predicts the surface accessibility, secondary structure, disorder, and phi/psi dihedral angles of amino acids in an amino acid sequence.

13. Submit New Questions or New Proteins
The SUBMISSION page allows users to submit information about new proteins, with required fields marked by a red asterisk. Upon receiving the user's submission, we will commence the submission request and contact the user if necessary.